Why Your Electrical Fuse Box Matters for Home Safety
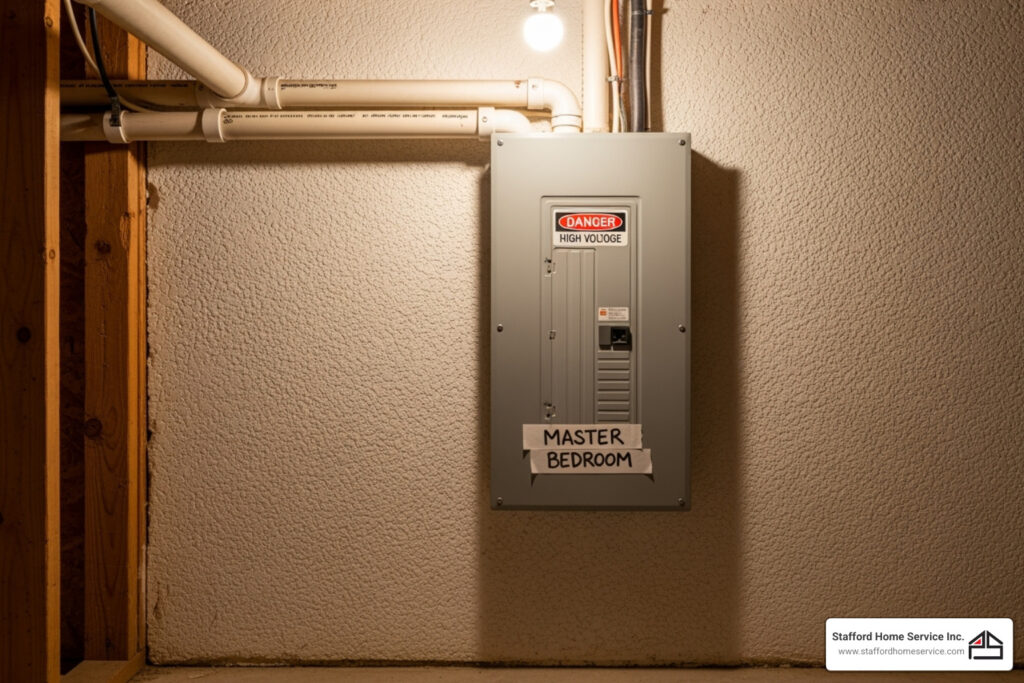
An electrical fuse box is the central hub that controls and protects your home’s electrical circuits. It prevents dangerous overloads by cutting power when circuits draw too much electricity, protecting your home from fires and electrical damage.
Quick Facts About Electrical Fuse Boxes:
- Function: Protects circuits from overcurrent to prevent fires
- Location: Usually in utility rooms, garages, or basements
- Capacity: Older boxes handle 60 amps vs. 200 amps for modern panels
- Safety: Uses disposable fuses that must be replaced when they blow
- Age: Common in homes built before the 1970s; now largely obsolete
If your home still has an old fuse box, you’re relying on 60+ year old technology that may not handle today’s electrical demands safely. Unlike modern circuit breaker panels that reset with a switch, fuse boxes require you to replace the fuse every time one blows. More importantly, they lack modern safety features like ground fault protection and arc fault detection, which are crucial for preventing electrical fires and shock hazards. Understanding your fuse box is the first step toward making informed decisions about your home’s electrical safety.
Understanding Your Home’s Electrical Fuse Box and Its Components
Your electrical fuse box is mission control for your home’s electrical system, acting as a protective gatekeeper between the main power lines and the circuits in your walls. When a circuit overloads or a short circuit occurs, the fuse box cuts power to prevent dangerous situations like electrical fires. While some homeowners call it a “fuse box,” electricians may use terms like consumer unit or circuit breaker panel, but they all serve the same purpose: distributing electricity safely.
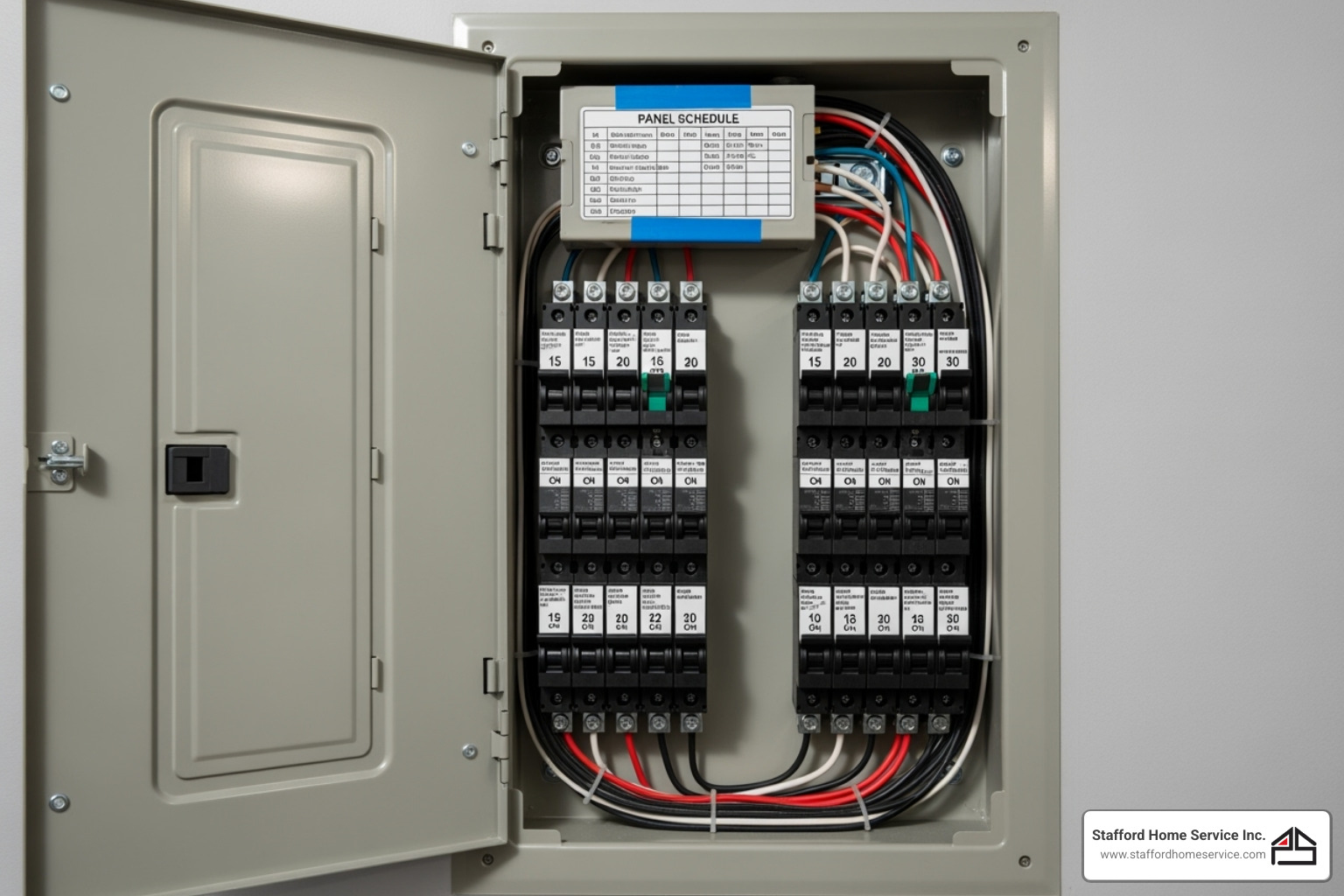
Key Components of an Electrical Fuse Box
Let’s review the key parts inside your electrical panel:
The main switch, usually a large switch at the top, controls all electricity coming into your home. It’s your primary safety shut-off for emergencies or electrical work.
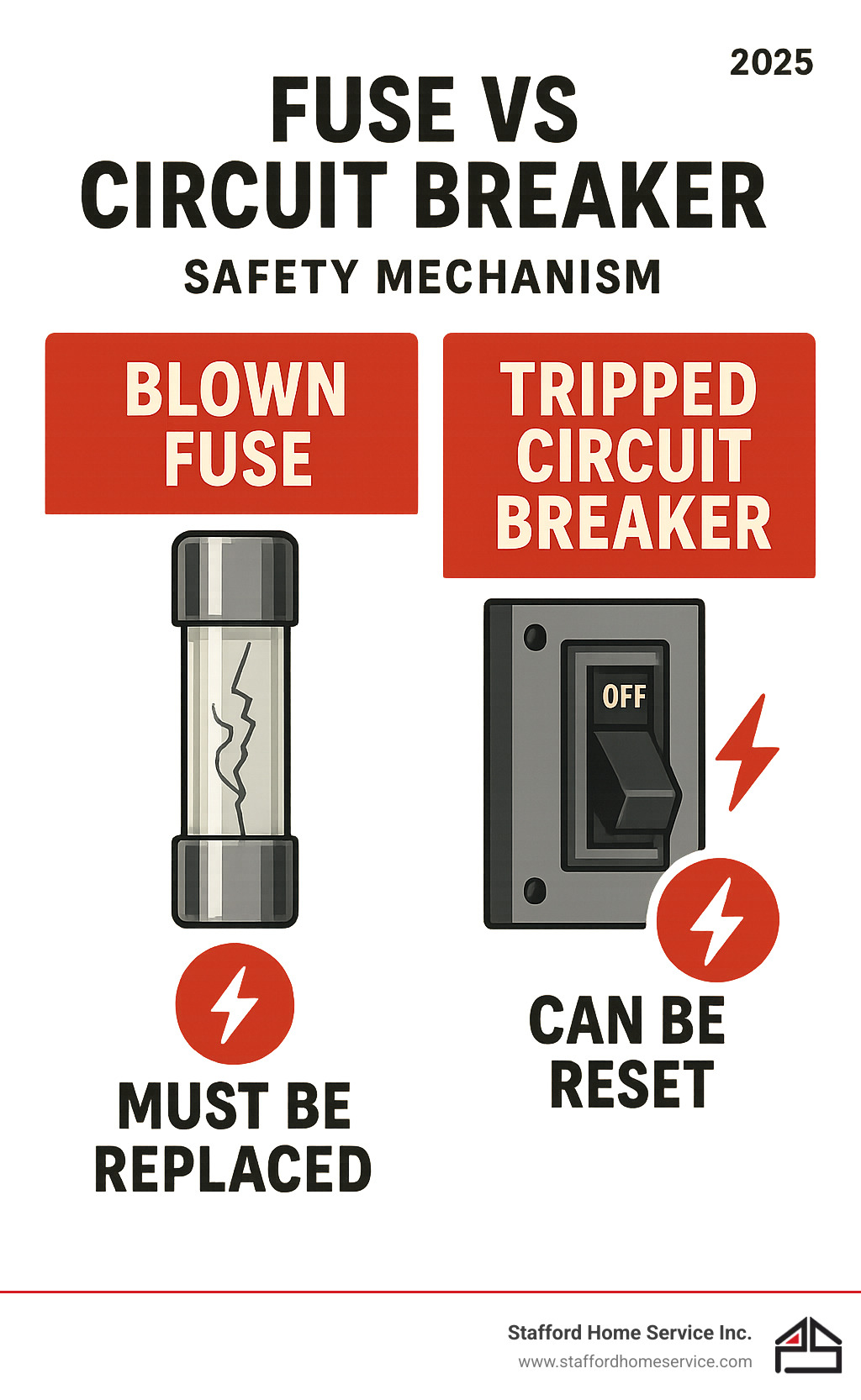
Individual circuits are protected by either fuses or circuit breakers. Traditional fuses contain a metal strip that melts (or “blows”) when too much current flows through, disconnecting the circuit. A blown fuse must be replaced with a new one of the correct amperage.
Modern systems use Circuit Breakers (MCBs), which automatically flip off when they detect an overload. They can be reset by simply flipping the switch back on after fixing the issue.
Residual Current Devices (RCDs) are critical safety features in modern systems. They detect tiny imbalances in current that could indicate an electric shock and cut power in milliseconds to prevent serious injury. You should test your RCDs every three months using the test button. You can learn more about Residual Current Devices (RCDs) explained.
Behind the scenes, bus bars are the metal conductors that carry electricity from the main switch to the individual fuses or circuit breakers, powering each circuit in your home.
Understanding these components helps you appreciate the sophisticated safety systems protecting your home every day. When everything works together properly, your electrical fuse box quietly keeps your family safe while powering your modern lifestyle.
Fuse Box vs. Modern Circuit Breaker Panel: What’s the Difference?
Many homeowners use “fuse box” and “circuit breaker panel” interchangeably, but they are very different systems. Comparing them is like comparing a rotary phone to a smartphone—one is far safer and more convenient.
| Feature | Old-Style Fuse Box | Modern Circuit Breaker Panel |
|---|---|---|
| Reset Method | Disposable fuses that must be replaced when blown | Resettable switches that trip and can be flipped back |
| Safety | Limited protection against shocks and fires; prone to overfusing; older wiring often ungrounded | Improved safety with GFCI and AFCI technology; better fire and shock protection; modern wiring typically grounded |
| Capacity | Typically 60-amp total capacity, insufficient for modern electrical demands | Commonly 200-amp total capacity, designed for today’s high-power appliances and electronics |
| Convenience | Requires spare fuses and tools for replacement; inconvenient during frequent trips | Easy to reset with a flip of a switch; no need for replacements |
| Technology | Older, less sophisticated overcurrent protection; lacks modern safety features | Advanced overcurrent protection; includes Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs) and Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCIs) |
Key Differences Explained
The most obvious difference is convenience. With a fuse box, a blown fuse must be unscrewed and replaced. A circuit breaker simply needs to be flipped back on after you resolve the issue.
Capacity is another major factor. Most older fuse boxes provide 60 amps of power, which is insufficient for modern homes filled with computers, large appliances, and air conditioning. A modern 200-amp panel can safely handle these high demands.
Most importantly, modern panels offer superior protection. They incorporate GFCI technology (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters) to prevent electrocution and AFCI technology (Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters) to stop electrical arcs that cause house fires. An old electrical fuse box simply cannot provide these life-saving features. It’s running on obsolete technology that doesn’t meet today’s safety standards.
Warning Signs: When to Replace Your Fuse Box
An aging electrical fuse box will show signs of wear that can lead to serious safety hazards. Knowing how to spot these issues is key to protecting your home.
Here are the warning signs that your fuse box needs professional attention:
- Frequent Blown Fuses: If you’re constantly replacing fuses, your system is likely overloaded or has an underlying fault.
- Flickering Lights: Flickering or dimming lights, especially when appliances turn on, can indicate a deteriorating electrical system.
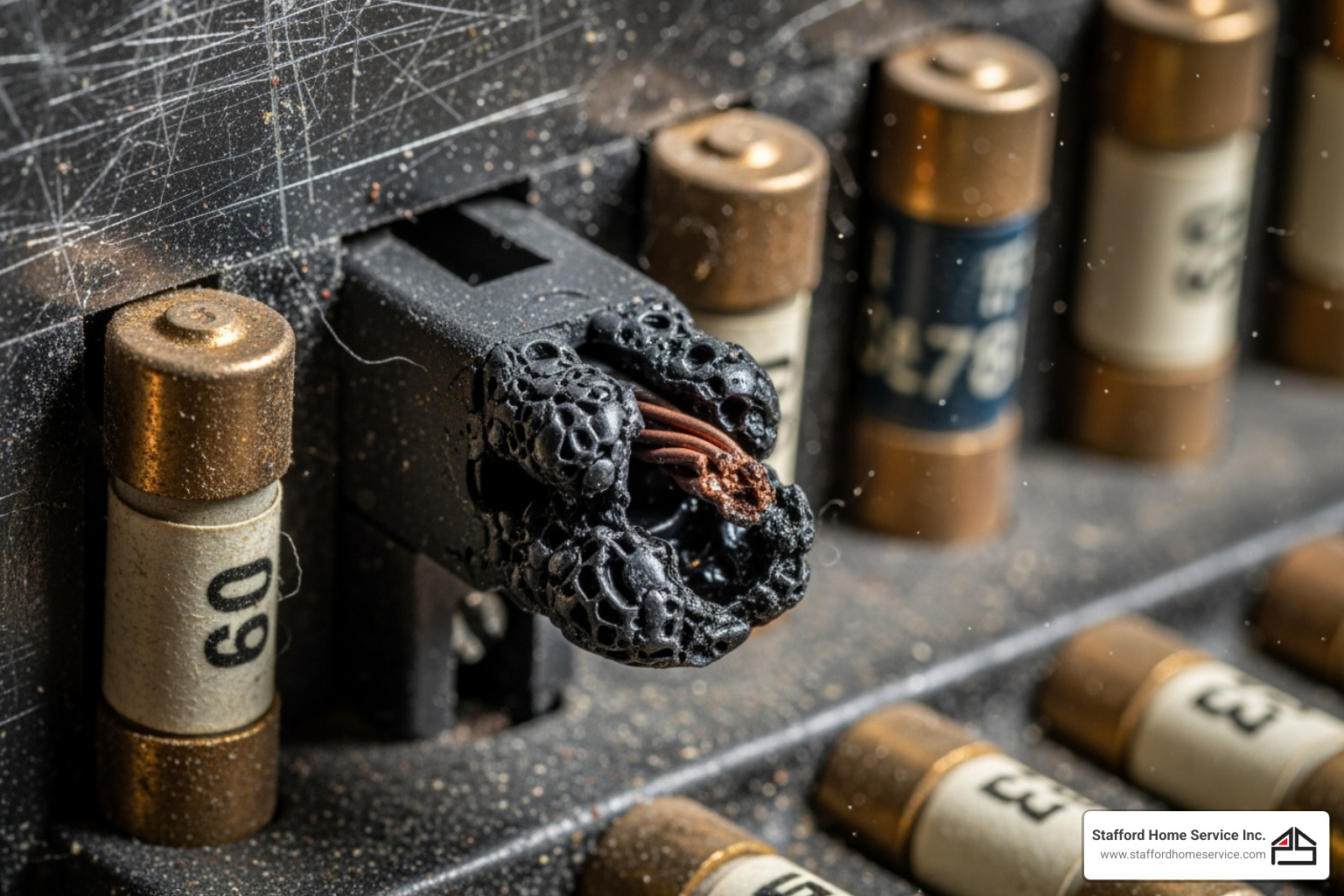
- Overheating: Melted fuses, burnt terminals, or discoloration around the fuse box are dangerous defects that require an immediate call to an electrician.
- Strange Smells or Sounds: A burning plastic smell or any buzzing, crackling, or popping sounds from the fuse box signal a serious problem like overheating or arcing.
- Melted Wires or Discolored Outlets: Scorched outlets or melted wire insulation point to overheating circuits, often stemming from a faulty fuse box.
- Loose Fuses: Fuses should fit snugly. Loose connections can cause intermittent power and create a fire hazard.
Common Problems with an Electrical Fuse Box
Beyond these signs, older fuse boxes have inherent issues:
- Overloaded Circuits: Older 60-amp systems can’t handle the demands of modern 200-amp lifestyles, leading to constant overloads.
- Deterioration with Age: All electrical components degrade over time, increasing the risk of faults. Fuse boxes over ten years old may show signs of deterioration.
- Lack of RCD Protection: Many older fuse boxes lack Residual Current Devices (RCDs), which are vital for preventing life-threatening electrical shocks.
- Asbestos Flash Guards: Some very old fuse boxes contain asbestos, a serious health hazard if disturbed. You can read more about the dangers on the HSE website. Professional inspection is crucial.
- Insufficient Capacity: If your fuse box is full or can’t handle a new appliance like an EV charger, it’s time for an upgrade.
- Known Hazardous Panels: Panels from manufacturers like Zinsco or Federal Pacific are known fire hazards and should be replaced immediately.
If you notice any of these signs, contact a professional. Attempting DIY fixes on a faulty fuse box puts your home and family at severe risk.
The Fuse Box Replacement Process: Costs, Timeline, and Requirements
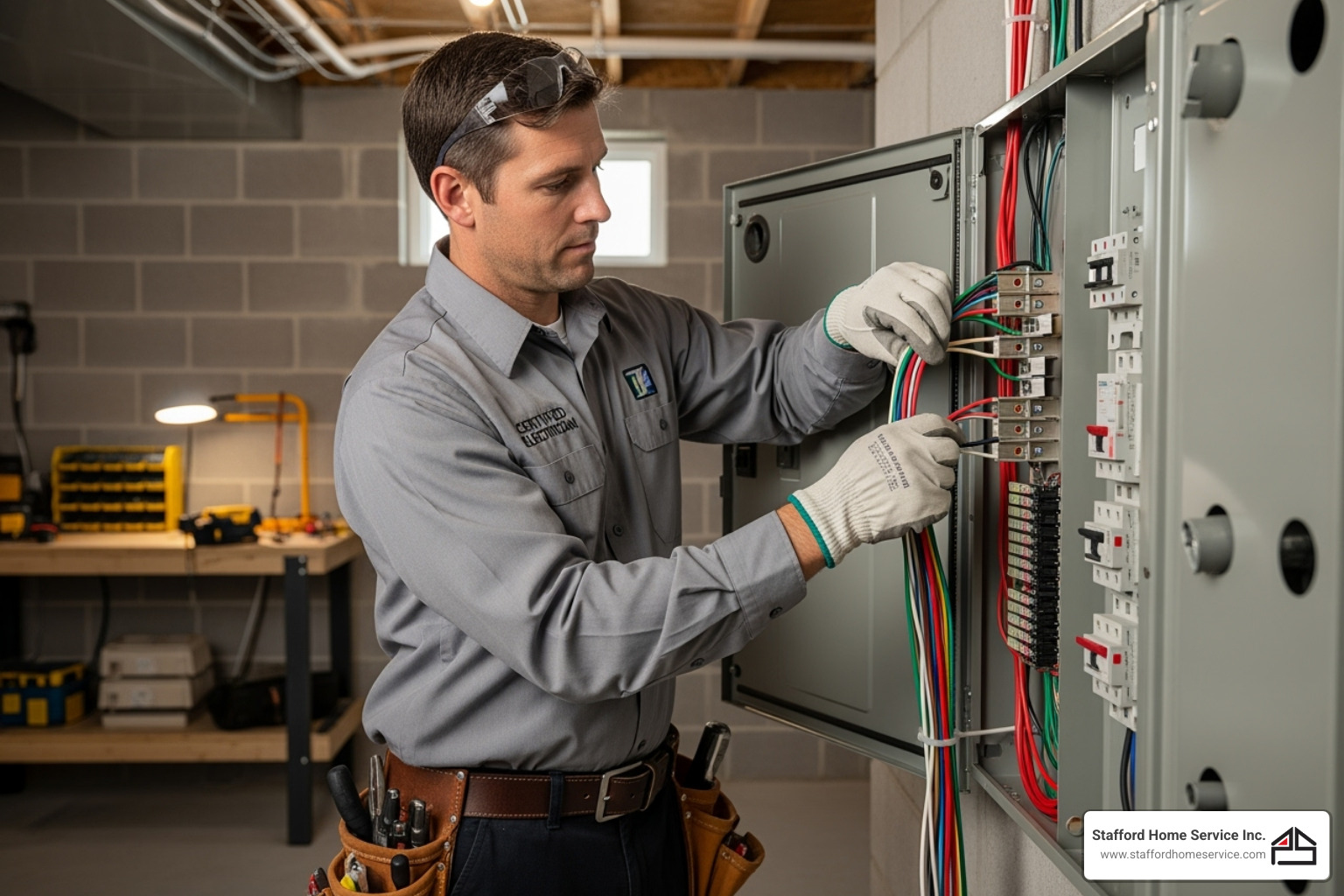
Upgrading your old electrical fuse box to a modern circuit breaker panel is one of the smartest investments for your home’s safety and functionality. While it may seem like a major project, it’s routine work for a qualified electrician.
Professional Installation
Replacing an electrical fuse box is not a DIY project. It involves working with your home’s main electrical supply, which is extremely dangerous without specialized training and tools. A licensed electrician ensures the work complies with the National Electrical Code (NEC) and local regulations, guaranteeing a safe and reliable installation.
A professional handles all aspects of the job, including:
- Permitting: We guide you through any required municipal permits.
- Compliance Certificates: You’ll receive documentation confirming your new panel meets all regulatory standards, which is valuable for insurance and home resale.
- Safe Installation: This includes safely disconnecting the old system, installing the new panel, and ensuring proper grounding and wiring connections.
How Much Does a Fuse Box Replacement Cost?
The cost of a fuse box replacement depends on several factors. We can’t provide a specific quote without an in-person assessment, but here are the main variables:
- Panel Cost: The price varies by brand, size, and features like built-in surge protection.
- Labor Costs: This reflects the electrician’s time and expertise to perform the installation safely and correctly.
- Wiring Upgrades: If existing wiring is outdated or damaged, it may need to be upgraded to handle the new panel’s capacity. This is often the largest variable.
- Service Amperage Upgrade: Many homeowners upgrade from 60 amps to a 200-amp service, which may require a new main service cable from the utility.
- Additional Safety Devices: Costs may include adding new dedicated circuits, GFCI outlets, or AFCI breakers as required by modern codes.
For more detailed cost information, you can check out resources like How Much Does It Cost to Replace an Electrical Panel?.
How Long Does an Upgrade Take?
Most electrical fuse box replacements can be completed in about half a day. The exact timeline depends on factors like your property’s size, the condition of your existing wiring, and the accessibility of the panel. If extensive rewiring is needed, the job will take longer. We always provide a clear timeline upfront and work efficiently to minimize disruption.
Frequently Asked Questions about Electrical Fuse Boxes
Homeowners often have questions about their electrical fuse box. Here are answers to the most common ones we hear.
Do I have to replace my fuse box?
While not always legally required, we strongly recommend replacing an old fuse box for several key reasons. Modern circuit breaker panels offer superior safety features like GFCIs and AFCIs that prevent fires and shocks—protections your old fuse box lacks.
Furthermore, most old fuse boxes have a capacity of only 60 amps, which is insufficient for the demands of a modern home. This can lead to overloads and fire risks. Over time, age and deterioration can cause connections to loosen and corrode. Finally, many insurance companies may charge higher premiums or require an upgrade for homes with outdated electrical systems. A modern panel is also a significant selling point when you decide to move.
Can I replace a fuse box myself?
Absolutely not. Replacing an electrical fuse box is a complex and dangerous job that should only be performed by a licensed electrician. You will be working with the main power supply to your home, which carries enough voltage to cause serious injury or death.
Proper installation requires expert knowledge of electrical codes and safety standards to prevent fire and electrocution hazards. DIY work often fails inspections and can void your homeowner’s insurance. Hiring a licensed and insured professional ensures the job is done safely, correctly, and is backed by a warranty. For your family’s safety, always leave this work to the pros.
Why does my fuse box keep tripping?
A frequently tripping fuse or breaker is a warning sign from your electrical system. The most common causes include:
- Overloaded Circuits: This is the most frequent issue. It happens when you plug too many high-power appliances into a single circuit, causing it to draw more current than it can handle. The fuse blows to prevent wires from overheating.
- Short Circuits: This is a more serious problem where a hot wire touches a neutral wire, causing a massive surge of current that trips the protection instantly. This can be caused by damaged cords or faulty wiring.
- Ground Faults: This occurs when a hot wire touches a grounded object, like a metal box. GFCIs are designed to detect this and shut off power to prevent dangerous shocks.
- Faulty Appliance: A single appliance with damaged internal wiring can draw too much power and cause the circuit to trip repeatedly.
- Furnace Issues: If your furnace fuse keeps blowing, it could be due to a dirty blower motor, loose wiring, or a failing component. This requires an HVAC professional.
If you’re dealing with frequent tripping, try to identify the cause by unplugging devices. For any persistent issues, call a professional for a safe diagnosis and repair.
Secure Your Home with a Professional Electrical Upgrade
Your home should be a safe haven, but an outdated electrical fuse box can pose a hidden risk. Upgrading to a modern circuit breaker panel is not just about convenience; it’s about protecting your family and your home.
When to Call an Electrician
If you notice frequent blown fuses, flickering lights, strange smells, or any visible damage to your electrical system, it’s an urgent call for action. These signs indicate your system is struggling and potentially unsafe. Even without obvious problems, if your home was built before the 1980s and has its original fuse box, an upgrade is a wise investment. Old systems were not designed for the high-demand devices we use every day.
Importance of Certified Professionals
Electrical work requires precision and expertise. A mistake can have devastating consequences. Certified electricians have the training, understand local building codes, and carry the proper insurance to ensure the job is done right. When you hire a professional, you’re investing in peace of mind, knowing your family is protected by a safe, reliable electrical system.
Ensuring Home Safety
At Stafford Home Service Inc., we understand that quality workmanship is essential for your family’s safety. We back every job with our Daikin Comfort Promise and offer financing options because we believe every homeowner deserves access to critical safety upgrades. Our commitment to customer satisfaction means we aren’t finished until you are completely confident in your home’s electrical system.
Don’t let an aging electrical fuse box put your home and family at risk. Modern panels with ground fault protection, arc fault detection, and 200-amp capacity are essential for today’s homes.
Ready to take the next step toward a safer home? We proudly serve homeowners throughout Minneapolis, Edina, Golden Valley, Minnetonka, Plymouth, St Louis Park, and all across Minnesota. Schedule your professional electrical service today and let us help secure your home for years to come.